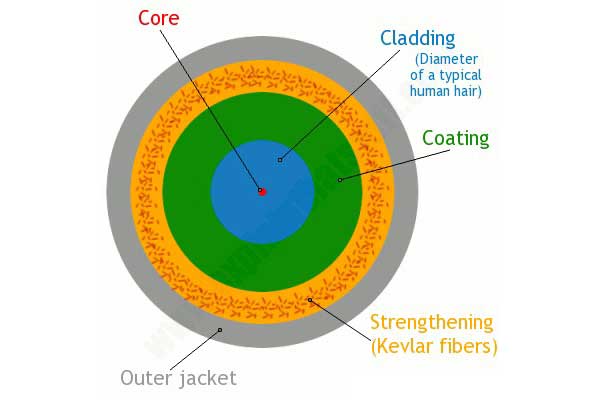
Optical fiber communication is a communication method that uses optical fiber as a medium to transmit optical signals from one place to another. The signal is converted from an electrical signal to light in the optical fiber and converted back into the electrical signal at the receiving end.
The optical signal is a carrier wave modulated to carry information. The data can be in the form of audio, video, or telemetry data, which will be sent over long distances or local area networks. Compared to electrical cabling, fiber optic cables are more suitable for high bandwidth, long-distance, or anti-electromagnetic interference, it has been widely used by many telecommunications companies to transmit telephone signals, Internet communication, and cable television signals.
1. How does Fiber Optic Communication work?
The process of optical fiber communication transmits signals in the form of light. The signals are first converted from electrical signals into light and transmitted, and then converted back into the electrical signal on the receiving side.
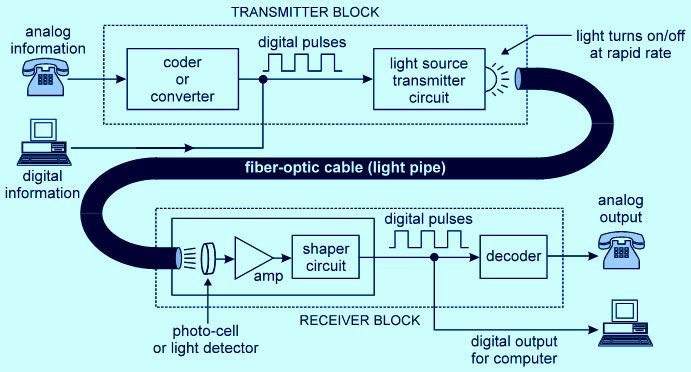
Transmitter side
On the transmitter side, analog data will be first sent to the encoder or converter circuit, which converts the analog signal into digital pulses 0, 1, 0, 1… (depending on the data), and pass through a light source transmitter circuit. If the input is digital, the signal will be directly converted into a light waveform through the light source sending circuit.
Optical Fiber Cable
After receiving the light wave from the transmission circuit, the fiber optic cable transmits it from the source location to the destination and finally received it in the receiving block.
Receiver Side
Photocells are also called photodetectors, which receive light waves from optical fibers, and amplify and convert them into suitable digital signals. An analog signal will require a decoder circuit to meet the requirement of the output source, and the digital signal doesn’t need to change anymore.
The whole process of transmitting electrical signals from one point to another, converting them into light, and using optical fibers as the transmission source is called optical fiber communication.
2. Advantages of Optical Fiber
The fact proved that fiber optic cables have replaced copper wires to become a better choice for high bandwidth, long-distance, or anti-electromagnetic interference. Here are the main advantages of optical fiber:
- Large Transmission capacity: By using a small part of the theoretical capacity, a single silicon fiber can carry hundreds of thousands of telephone channels.
- Small Losses: In modern single-mode silicon fiber, the signal of about 0.2 dB/km will be lost, so the signal of tens of kilometers can be bridged without amplifying the signal.
- Easy Amplification: If a very large transmission distance is required, a large number of channels can be re-amplified in a single fiber amplifier.
- Low Cost: Since a huge transmission rate can be achieved, the cost of each transmission bit can be very low.
- Light Weight: Fiber-optic cables are much lighter than electrical cables
- No interference: Optical fiber is not affected by cable problems such as ground wire and electromagnetic interference.
3. Why use light for communication
To be precise, it is the laser light that is used for communication. Common light has many wavelengths, if used for communication it would produce a powerless beam.
Different from common light, laser light is a single wavelength light source, which makes it has a more powerful beam as output. Less dispersion, more signal transmission, and less time consumption making light a good source of communication.
4. Characteristics of Fiber Optic Communication
In fiber-optic communications, light is transmitted as a signal inside the fiber optic cable. This communication method has some important characteristics, which, make it a good communication method.
- Bandwidth: The dispersion of single laser light means that a large number of signals (information transmission in bits) can be transmitted per second, thereby obtaining high bandwidth over long distances.
- Smaller diameter: The diameter of the fiber optic cable is approximately 300 microns.
- Light-weight: Optical fiber is lighter than copper wire.
- Long-distance signal transmission: Since the laser is not scattered, it is easy to transmit over long distances.
- Low attenuation: The laser travels through the optical fiber, which is made of glass, and the transmission signal loss is only 0.2 dB/km.
- Transmission security: Optical encryption and the absence of electromagnetic signals make data safe on optical fibers.
5. Applications of Optical Fiber
Optical fiber communication is mainly used in the telecommunications industry, using optical fiber for telephone signal transmission, Internet communication, and cable television signal transmission. Besides, optical fiber has been used everywhere in our diary life, including in homes, industries, and offices for long-distance as well as for small distance communication.